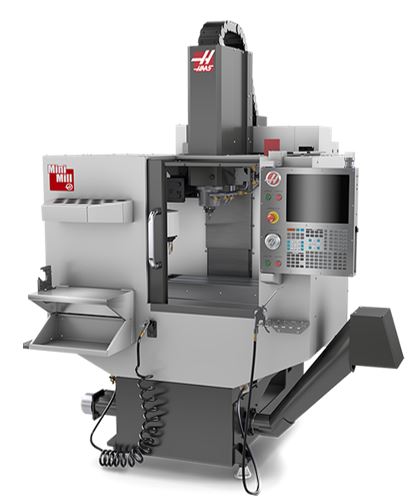
The Laboratory of Machine Tools and Automation is equipped with a Haas MiniMill vertical milling center. This machine features state-of-the-art CNC equipment and is equipped with a 10-position tool magazine. It allows for complex machining operations in three axes, including milling, drilling, boring, and threading. Additionally, the machine is used for training activities in the programming and operation of CNC machine tools.
The laboratory also includes a Haas simulator, which emulates the control panels of both milling and turning CNC machines. This simulator is a high-performance device that effectively complements practical activities in training courses.
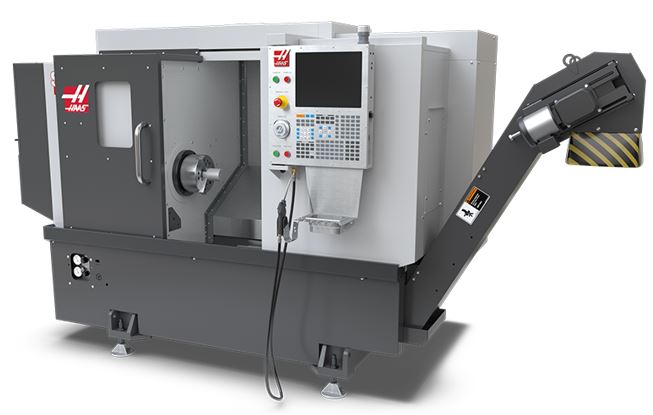
Furthermore, the laboratory is equipped with a UMC-500 Vertical Machining Center. This center features five axes: three translational axes (X, Y, and Z) and two rotational axes (B and C). Five-axis machining offers a way to reduce the number of setups and increase precision for complex parts, making it the perfect solution for 3+2 machining and simultaneous five-axis machining of smaller parts.
An important advantage in machining complex parts is the high-capacity side tool magazine, which holds 30+1 tools. Additionally, the machine is equipped with an intuitive wireless probing system, an automatic workpiece zero-point setting system from RENISHAW, which also serves to automatically measure tool lengths.
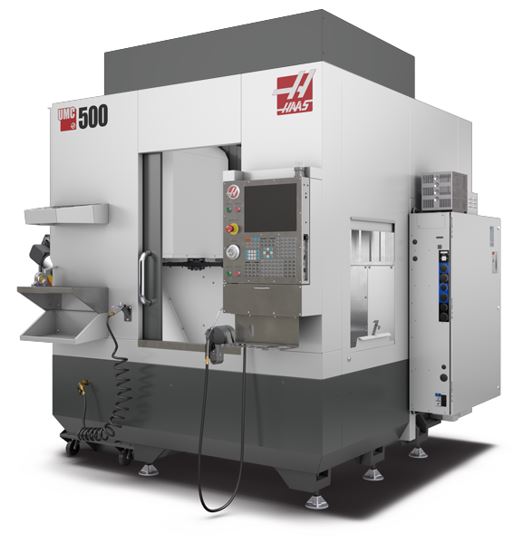

The laboratory is also equipped with a high-performance turning center from the Haas ST15Y series with five axes, offering high flexibility, extreme rigidity, and high thermal stability. The turning center features five axes: three translational axes (X, Y, and Z), one rotational axis (C), and an additional translational axis (B). In addition to the main spindle, the machine also has a secondary spindle.
This turning center is highly capable, offering a generous workspace despite its small footprint, allowing for the machining of large diameters. The main spindle can operate at speeds of up to 4000 rotations per minute. The turret head and driven tool assembly can hold up to 12 tools. The turning center is equipped with an automatic tool presetter and an intuitive wireless probing system for lathes.

The laboratory also includes the General Numeric 5AX five-axis CNC machining center. This is a modular CNC machine tool equipped with an open-architecture Linux CNC controller. The machining center allows for research related to the kinematics and programming of multi-axis machine tools.
The modular construction allows for easy addition, modification, or removal of numerical axis modules. The open software architecture of the CNC controller also enables advanced research on the control of numerical axes using various control strategies.
Additionally, the laboratory is equipped with manually operated machine tools for machining parts through the cutting process, including a Bernardo Profi 400 V precision lathe with digital display, a Bernardo KF 25 Pro drilling and milling machine with three axes and digital display, and a Bernardo TB 20 T bench drill.
The Laboratory of Machine Tools and Automation is also equipped with a Bernardo DSA 200 bench grinder, a bench shear for cutting sheet metal, a Bernardo EBS 115 band saw, and a Bernardo AC12 mobile compressor. Additionally, the laboratory contains various sets of cutting tools, such as drills, step drills, countersinks, reamers, milling cutters, lathe tools, ER 40 collet chucks for milling cutters with diameters between 3 and 25 mm, and sets of taps and dies.
Research on modern manufacturing processes is facilitated by the combined milling and 3D scanning equipment, the Roland Modela MDX 15, which is equipped with both a scanning head and a milling head, easily interchangeable. Depending on the installed unit, the equipment can be used as a 3D scanner or a mini milling center. The Roland Modela MDX 15 allows the creation of a 3D model of a physical object through scanning and then machining a new replica of the scanned object using reverse engineering on the same equipment.
The laboratory conducts research on the precision of technological processing equipment. For this purpose, the Renishaw QC 10 kit is used to evaluate the accuracy of CNC machine tools. Utilizing a high-precision inductive sensor and dedicated software, it allows for the evaluation of errors in circular interpolation and the determination of necessary measures to reduce them.
The laboratory also houses a General Numeric S6 CNC equipment, a modular industrial CNC system used for equipping energy beam processing machines (oxy-acetylene flame, laser, plasma, water jet).
For the study of computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) techniques, as well as for the operation and utilization of the aforementioned equipment, the laboratory is equipped with specific software packages, including Roland Modela 4.0, FastCAM (energy beam processing), SprutCAM (milling and turning processes), NC Tuner (CNC program optimization), as well as a 10-seat network license for the well-known CNC program creation and simulation software, CIMCO Edit.
The laboratory also features hardware that enables the creation of modular, flexible automated manufacturing systems, such as the Festo Edutrainer, an educational platform designed to facilitate the learning and application of automation and industrial control concepts. The system comprises six Siemens Simatic S7-1215C programmable logic controllers (PLCs), offering advanced control and monitoring capabilities for processes. Additionally, six Siemens HMI KTP700 operator panels provide an intuitive interface for users, facilitating interaction and control of automated systems. The six Siemens XB005 Ethernet switches ensure robust and reliable connectivity between system components, ensuring efficient and fast communication within the automation network. The system includes TIA Portal V18 licenses, providing an integrated and advanced programming environment for designing, programming, and diagnosing automation systems.
In research, this equipment can be used for developing and testing new technologies, simulating and optimizing complex industrial processes, and rapid prototyping of new concepts. It can also support interdisciplinary research, combining engineering, computer science, and robotics to develop advanced solutions in emerging fields such as industrial IoT and cyber-physical systems. The Edutrainer is a valuable tool for continuous training, contributing to the development of necessary skills in advanced research and facilitating collaborations between universities and industry.
Among the models available in the laboratory are Siemens Simatic S7 300 (4 units), S7 200 (1 unit), Omron CPM2A (1 unit), Omron CP1E (1 unit), Allen Bradley Micro 850 (1 unit), as well as Telemecanique, Bernecker & Reiner, and Moeller PLCs (1 unit each).
The programming of the PLCs in the laboratory is done using specific software packages, such as Siemens TIA Portal V18, Simatic STEP 7 MicroWin, Allen Bradley by Rockwell Factory Talk, Telemecanique Twidosoft, and Omron Syswin.
The automation laboratory conducts research on motion control systems aimed at developing modular and reconfigurable CNC equipment. One of the experimental stands used for this purpose is the three-axis motion control system composed of Bernecker & Reiner synchronous servomotors with permanent magnets, equipped with digital transducers on the motor shaft, variable speed drives (servo drives), and programming software. The system has an architecture specific to industrial CNC equipment but is realized in an open structure, allowing research on the study and implementation of various motion control strategies. Additionally, the laboratory has a one-axis motion control system with Technosoft ISCM 4085 DSP (digital signal processing) boards. This development system allows the study through simulation and experimental testing of advanced motion control strategies implemented at the signal processor level on the DSP board.